Spring Boot Startup Process
Spring启动间都发生了什么?
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/3.0.x/reference/overview.html
Springboot作为我们最常用的一款框架,其启动流程、注册机制、容器管理、bean加载、启动后是如何保持服务一直运行的,这些问题你都清楚嘛?
如果你也不清楚,那么我们来一起看看SpringBoot是如何启动的吧,在这里你会了解到Springboot是如何启动的,并且是如何支持上述问题的。
问题清单
- 启动流程
- 注册机制
- 容器管理
- bean加载过程
- 日志框架
- 启动后是如何保持服务一直运行的?
流程图我后续会整理到:https://www.processon.com/diagraming/63e39fc810a38f1c1873131e
接下来我们跟踪源码进入Spring的启动过程,看看Spring启动时都发生了什么?
1.1 入口
// 首先,我们从SpringApplication类开始,SpringApplication类是SpringBoot的入口点,SpringBoot启动时,会调用SpringApplication.run方法
// SpringApplication.run方法会调用SpringApplication.run方法,SpringApplication.run方法会调用SpringApplication.run方法,SpringApplication.run方法会调用SpringApplication.run方法,SpringApplication.run方法会调用SpringApplication()
@SpringBootApplication
public class BootProcessApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.1启动入口
SpringApplication.run(BootProcessApplication.class, args);
}
}
1.2 调用SpringApplication.run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
// 调用SpringApplication.run方法
return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
// 调用SpringApplication.run方法,声明一个SpringApplication对象,对对象的属性进行初始化
return (new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 获取应用类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
// 调用SpringApplication.run方法,这个方法可以让我们看到Spring启动期间大致做了什么事
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 定义全局的计时器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
// 开始计时
stopWatch.start();
// 定义Spring应用上下文的变量
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 定义SpringBoot异常报告栈
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
// 1.3 配置headless mode,详情可以参考下面的注释
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
// 1.4 获取SpringBoot监听器并启动监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
// 获取SpringBoot启动参数: []
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 1.5 准备SpringBoot环境变量
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印SpringBoot启动banner
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
// 1.6 创建Spring应用上下文
context = this.createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
// 2.1 准备SpringBoot上下文
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 3.1 刷新SpringBoot上下文
this.refreshContext(context);
// 刷新完成后的动作,空方法!!
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
// 4.1 运行SpringBoot上下文
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners) null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}
1.3 配置headless mode
// 1.3 配置headless mode
private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
// 结合上下文,可以知道,这里是给java.awt.headless设置默认值(根据上下文可知):true
// java.awt.headless参数的意义是:在没有显示器的、键盘、鼠标等设备的情况下,程序可以运行
// 可以通过:System.setProperty("java.awt.headless", "true"); 或者添加启动参数:java -Djava.awt.headless=true
// Headless mode is a system configuration in which the display device, keyboard, or mouse is lacking.
// Sounds unexpected, but actually you can perform different operations in this mode, even with graphic data.
System.setProperty("java.awt.headless", System.getProperty("java.awt.headless", Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
}
1.4 获取SpringBoot监听器并启动监听器
// 1.4 获取SpringBoot启动监听器
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[]{SpringApplication.class, String[].class};
// 1.4.1 定义SpringBoot启动监听器
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
// SpringApplicationRunListener,跟踪源码可以看到,这个接口的实现为EventPublishingRunListener
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
// 1.4.2 获取Spring工厂实例
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
// 这里获取到的classLoader是AppClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
/**
*
* @param type SpringApplicationRunListener
* @param parameterTypes SpringApplication.class, String[].class
* @param classLoader AppClassLoader
* @param args []
* @param names class的完整类名
* @return List<T>
* @param <T> 类
*/
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
// 1.4.2.1 遍历SpringBoot启动监听器
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
// 熟悉的代码,同样的反射构造
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
// 1.4.3 初始化SpringBoot启动监听器
class SpringApplicationRunListeners {
// 注意这里两个类是不一样的,不是递归调用哦
void starting() {
// 区别SpringApplicationRunListeners:SpringApplicationRunListener,可以这么理解,
// SpringApplicationRunListeners是SpringApplicationRunListener的集合(代理)
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}
}
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
default void starting() {
}
}
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
@Override
public void starting() {
// 广播一个新的事件:new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args),表示SpringBoot应用正在启动
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
}
有关监听器这里还有一些细节,其方法的具体意义跟其方法命名一致,即字面意思。
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
/**
* Called immediately when the run method has first started. Can be used for very
* early initialization.
*
* 翻译过来就是:在应用启动的时候调用,用于最开始的初始化
*/
default void starting() {
}
/**
* Called once the environment has been prepared, but before the
* {@link ApplicationContext} has been created.
* @param environment the environment
*/
default void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
}
/**
* Called once the {@link ApplicationContext} has been created and prepared, but
* before sources have been loaded.
* @param context the application context
*/
default void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* Called once the application context has been loaded but before it has been
* refreshed.
* @param context the application context
*/
default void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* The context has been refreshed and the application has started but
* {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and {@link ApplicationRunner
* ApplicationRunners} have not been called.
* @param context the application context.
* @since 2.0.0
*/
default void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* Called immediately before the run method finishes, when the application context has
* been refreshed and all {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and
* {@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners} have been called.
* @param context the application context.
* @since 2.0.0
*/
default void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* Called when a failure occurs when running the application.
* @param context the application context or {@code null} if a failure occurred before
* the context was created
* @param exception the failure
* @since 2.0.0
*/
default void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
}
}
1.5 准备SpringBoot环境变量
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 配置环境变量
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 监听器发布 程序环境准备已完成
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
@SuppressWarnings("all")
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
// Servlet环境,构造器
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
1.6 创建Spring应用上下文
// 上下文变量,初始化为null
private Class<? extends ConfigurableApplicationContext> applicationContextClass;
// 1.10 创建Spring应用上下文
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
// 初次创建时applicationContextClass为null
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
// 启动时,因为带了spring-boot-starter-web依赖,所以在启动时,webApplicationType为SERVLET
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
// 实例化上下文,通过反射去调用方法的构造方法进行实例化,在这里有很多需要注意的地方,具体如下
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
1.6.1 实例化content
接上文,(ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass) 看似简单的一段代码,实则中间发生了好多你不一定知道的事情,下面就让我们来一探究竟吧。
跟代码往下走你可以发现最终的目的为org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 类声明一个新的实例
而这个类的实例化过程如下
public class AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext extends ServletWebServerApplicationContext
implements AnnotationConfigRegistry {
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
private final Set<Class<?>> annotatedClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>();
private String[] basePackages;
/**
* Create a new {@link AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext} that needs
* to be populated through register (a method in this class that I didn't show) calls
* and then manually refresh ( another method).
*/
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
// 想必大家都知道BeanDefinition在spring中是非常重要的
// 而这里给大家展示了应用上下文在初始化时是如何使用这些BeanDefinition的
// 注解bd读取器(加载器),类路径bd读取器(加载器)
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
}
我们可以看下这个类的继承与实现关系网
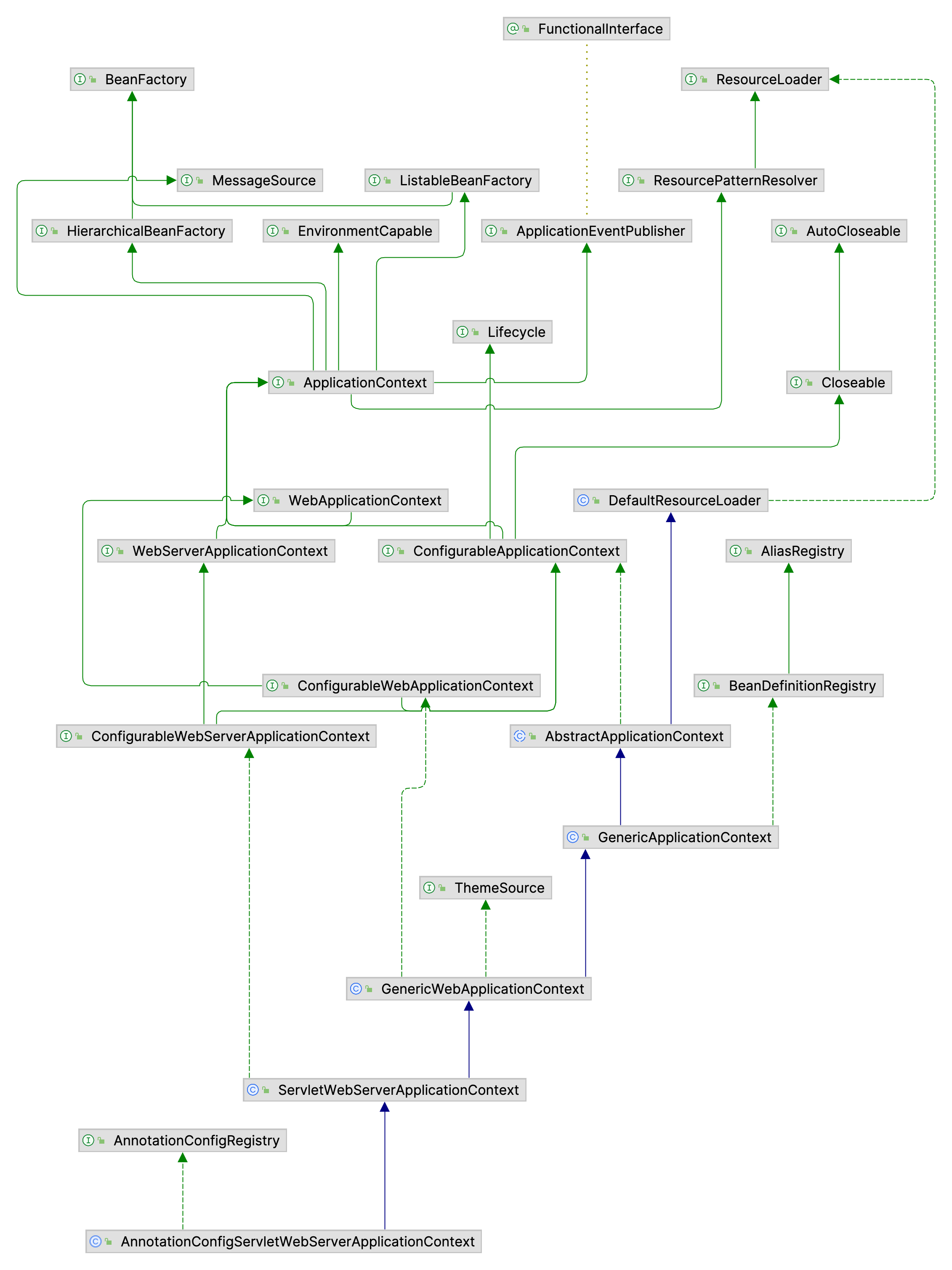
1.6.2 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader实例化过程
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = AnnotationBeanNameGenerator.INSTANCE;
private ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = new AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver();
private ConditionEvaluator conditionEvaluator;
/**
* Create a new {@code AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader} for the given registry.
* <p>If the registry is {@link EnvironmentCapable}, e.g. is an {@code ApplicationContext},
* the {@link Environment} will be inherited, otherwise a new
* {@link StandardEnvironment} will be created and used.
* @param registry the {@code BeanFactory} to load bean definitions into,
* in the form of a {@code BeanDefinitionRegistry}
* @see #AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry, Environment)
* @see #setEnvironment(Environment)
*/
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 在上面的步骤中,会调用这个方法,这个方法会调用下面的方法
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
/**
* Create a new {@code AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader} for the given registry,
* using the given {@link Environment}.
* @param registry the {@code BeanFactory} to load bean definitions into,
* in the form of a {@code BeanDefinitionRegistry}
* @param environment the {@code Environment} to use when evaluating bean definition
* profiles.
* @since 3.1
*/
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
// 上main都是正常的调用,没什么特殊的逻辑,直到这里
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
}
1.6.3 registerAnnotationConfigProcessors
注册注解配置处理器,这里面的代码需要着重看下,涉及到了一个beanDefinition是如何被添加到beanDefinitionMap的。
这里的Bean都是spring自己定义的bean。
// 最终方法会调用到这里
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
// 这里我们需要想一下,beanFactory是什么时候被放进来的?
// 答案看 1.6.3.1
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
// 依赖排序,通过设置@Priority来设置排序大小
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
// 设置自动注册情况的解析器
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
// 声明一个存储bean定义的holder的集合,重要的不是这个beanDefs,而是再添加到这个集合前做的处理registerPostProcessor
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 生成 BeanDef,准备
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
// 第一次
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
private static BeanDefinitionHolder registerPostProcessor(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, RootBeanDefinition definition, String beanName) {
definition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
// 调用Bean注册器将BeanDef注册进去,容器管理
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definition);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(definition, beanName);
}
// 发现是个接口,查看他的实现
void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
// 这里我们看一下registry的父类,一级一级往上找,找到了GenericApplicationContext,进去
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 进去
this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
// 找到实际执行的地方,注意,程序执行的时候,所有的bean都需要现在这里进行注册,不管是注解声明的bean还是配置声明的bean,还是系统指定的bean
// 在声明实现的时候都会到这里进行注册
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
} catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
// 先检查beanDefinitionMap里面是否存在,
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
// 如果存在
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
// 判断是否可以覆写
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
} else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
} else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
} else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
// 将bd放到map中
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
} else {
// 不存在在map中
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
// 锁一下
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
} else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
} else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}
1.6.3.1 解答
当我们在步骤1.6 中调用BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass)方法时,根据Java的双亲委派机制,一个子类被加载时,其父类一定会先被加载, 而AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的父类中的GenericApplicationContext在初始化时会声明一个beanFactory
1.6.4 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner实例化过程
同AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader.
2.1 准备SpringBoot上下文
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 设置上下文环境
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// 2.2 前置处理
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 2.3 程序上下文初始化
applyInitializers(context);
// 发布事件:程序进入prepared阶段
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
// 日志启动,在此之前日志系统不会输出内容
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans,添加启动时指定的单例bean,获取bean工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
// 发布事件:上下文进入loaded阶段
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
2.2 应用上下文的前置处理
// 应用上下文的前置处理
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected void postProcessApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// bean name 生成器
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR,
this.beanNameGenerator);
}
// 资源加载器
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
if (context instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
((GenericApplicationContext) context).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (context instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) {
((DefaultResourceLoader) context).setClassLoader(this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
}
}
// 添加转换服务
if (this.addConversionService) {
context.getBeanFactory().setConversionService(ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance());
}
}
2.3 初始化容器前的处理
// 如果我们有定制化需求,我们也可以自己实现这个接口
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 通过getInitializers() 我们可以知道Springboot内置的初始化器都有哪些
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(),
ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
// 接口
public interface ApplicationContextInitializer<C extends ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
/**
* Initialize the given application context.
* @param applicationContext the application to configure
*/
void initialize(C applicationContext);
}
// 实现
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
applicationContext.addApplicationListener(new ConditionEvaluationReportListener());
if (applicationContext instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
// Get the report early in case the context fails to load
this.report = ConditionEvaluationReport.get(this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
}
}
补充,如何添加自实现的initializer
@Order(199)
public class ApplicationContextInitializerUsage implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
// 日志
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(ApplicationContextInitializerUsage.class);
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 在初始化容器之前,可以对容器进行一些初始化操作
log.info("ApplicationContextInitializerUsage.initialize()");
log.info("applicationContext is active " + applicationContext.isActive());
log.info("applicationContext application name: " + applicationContext.getApplicationName());
log.info("applicationContext display name :" + applicationContext.getDisplayName());
log.info("applicationContext beanFactory : " + applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
log.info("applicationContext beanDefinition count :" + applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionCount());
log.info("applicationContext BeanDefinitionNames :" + Arrays.toString(applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()));
// log.info("applicationContext AutowireCapableBeanFactory :" + applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory());
log.info("applicationContext class loader :" + applicationContext.getClassLoader());
log.info("applicationContext startup date :" + applicationContext.getStartupDate());
}
}
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
public class BootProcessApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 启动入口
// SpringApplication.run(BootProcessApplication.class, args);
// 声明
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(BootProcessApplication.class);
// 注册启动器
app.addInitializers(new ApplicationContextInitializerUsage());
// 启动
app.run();
}
}
3.1 刷新SpringBoot上下文
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class SpringApplication {
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
// 检测勾子,如果为true,就注册一个结束前调用的勾子
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
} catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
// 进入实际的refresh
refresh((ApplicationContext) context);
}
@Deprecated
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
refresh((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext);
}
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
// ... 深入digging
}
上面的方法调用的是如下抽象类的方法,这里我们需要牢记类的继承关系图
// 最终会找一个抽象类,可以先大致了解一下这个类的方法大体干了什么
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 3.2 准备上下文刷新,即context
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 3.3 获取beanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 3.4 beanFactory的一些处理
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 3.5 beanFactory的前置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 3.6 调用容器中已经注册的工厂处理类,这里会将大部分的Bean都注册到容器内
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 3.7 注册 Bean 后处理器用于拦截bena的创建
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 3.8 初始化上下文的消息
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 3.9 初始化应用事件组播器,需要含有特定的bean才会执行具体的操作
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 3.10 初始化webserver(即内嵌tomcat,不完全意义)
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 3.11 检查并注册监听器类型的bean
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 3.12 实例化所有剩余的Bean(不包含懒加载的bean)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 3.13 发送完成刷新的消息
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
// 重置通用缓存
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
}
3.2 准备上下文刷新
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
} else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
// 初始化参数源,其实这里没做什么实际的事情
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
// 校验参数是否合法
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
} else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
3.3 获取beanFactory
其实这里获取到beanFactory就是context声明的时候创建的beanFactory。
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
// 返回的也是context中的beanFactory
return getBeanFactory();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
// 还记得这里的beanFactory是在什么时候声明的吗?
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}
在记一遍
// 在createApplicationContext的时候,初始化的类的父类GenericApplicationContext的初始化方法中,新声明了一个beanFactory,就是我们现在即将使用的
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
public DefaultListableBeanFactory() {
super();
}
}
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory
implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super();
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
}
}
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory extends FactoryBeanRegistrySupport implements ConfigurableBeanFactory {
public AbstractBeanFactory() {
}
}
// 每个类都有很多的变量在实例化的时候被初始化
3.4 beanFactory的一些处理
//
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 这里需要看一下,下一步要用到
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
3.5 beanFactory的前置处理
// 在AbstractApplicationContext里调用该方法,本身未实现,会调用子类的实现
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}
// 在调用这个方法的时候,会直接调用自己的这个方法
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 这里调用了父类的该方法
super.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
if (this.basePackages != null && this.basePackages.length > 0) {
this.scanner.scan(this.basePackages);
}
if (!this.annotatedClasses.isEmpty()) {
this.reader.register(ClassUtils.toClassArray(this.annotatedClasses));
}
}
// 父类的方法
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (this.servletContext != null) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
}
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
}
3.6 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors⭐
这里会从注解和配置文件加载 BeanDefinition
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 调用静态方法
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
// 如果存在 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 就调用
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// beanFactoryPostProcessors 是一个由beanFactoryPostProcessor组成的数组
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// 这里调用了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的方法,我们深入
// 接 3.6.1 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
} else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 一直到这里,上面的代码暂时没有很重要的
// !!!
// 3.6.2
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
} else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
} else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
} else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
} else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
3.6.1 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry⭐
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
// 具体内容看 Ⅰ
this.register(registry);
// 具体内容看 Ⅱ
this.configureConfigurationClassPostProcessor(registry);
}
// Ⅰ
private void register(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 声明了一个BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(SharedMetadataReaderFactoryBean.class, SharedMetadataReaderFactoryBean::new).getBeanDefinition();
// 将他注册到容器内
registry.registerBeanDefinition("org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory", definition);
}
// Ⅱ
private void configureConfigurationClassPostProcessor(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
try {
BeanDefinition definition = registry.getBeanDefinition("org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor");
definition.getPropertyValues().add("metadataReaderFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference("org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory"));
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException var3) {
}
}
Note
我们需要先了解下 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的作用,他其实就是一个Function call。
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean definition registry after its
* standard initialization. All regular bean definitions will have been loaded,
* but no beans will have been instantiated yet. This allows for adding further
* bean definitions before the next post-processing phase kicks in.
* @param registry the bean definition registry used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
// 继承于
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
3.6.2 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors⭐
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
// 还是上面提到的function call
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
}
public class ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,
PriorityOrdered, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
// 关键代码
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
}
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
// 候选
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
} else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
// 解析 3.6.3 parse
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}
3.6.3 parse⭐
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
try {
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// 解析
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
} else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
} else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex);
}
}
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
}
protected final void parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) throws IOException {
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(metadata, beanName), DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER);
}
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, Predicate<String> filter) throws IOException {
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);
if (existingClass != null) {
if (configClass.isImported()) {
if (existingClass.isImported()) {
existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);
}
// Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it.
return;
} else {
// Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import.
// Let's remove the old one and go with the new one.
this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);
this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);
}
}
// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);
do {
// 3.6.4 doProcessConfigurationClass 处理配置类
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
3.6.4 doProcessConfigurationClass⭐⭐⭐
就是这里对主类进行了加载
@Nullable
@SuppressWarnings("all")
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
// 先处理成员类,即依赖参数
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// 解析携带PropertySource的注解的类
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
} else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
// 处理ComponentScan注解
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
// 解析,看下面一段代码
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> parse(AnnotationAttributes componentScan, final String declaringClass) {
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this.registry,
componentScan.getBoolean("useDefaultFilters"), this.environment, this.resourceLoader);
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> generatorClass = componentScan.getClass("nameGenerator");
boolean useInheritedGenerator = (BeanNameGenerator.class == generatorClass);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(useInheritedGenerator ? this.beanNameGenerator :
BeanUtils.instantiateClass(generatorClass));
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxyMode = componentScan.getEnum("scopedProxy");
if (scopedProxyMode != ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {
scanner.setScopedProxyMode(scopedProxyMode);
} else {
Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> resolverClass = componentScan.getClass("scopeResolver");
scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(resolverClass));
}
scanner.setResourcePattern(componentScan.getString("resourcePattern"));
for (AnnotationAttributes filter : componentScan.getAnnotationArray("includeFilters")) {
for (TypeFilter typeFilter : typeFiltersFor(filter)) {
scanner.addIncludeFilter(typeFilter);
}
}
for (AnnotationAttributes filter : componentScan.getAnnotationArray("excludeFilters")) {
for (TypeFilter typeFilter : typeFiltersFor(filter)) {
scanner.addExcludeFilter(typeFilter);
}
}
boolean lazyInit = componentScan.getBoolean("lazyInit");
if (lazyInit) {
scanner.getBeanDefinitionDefaults().setLazyInit(true);
}
Set<String> basePackages = new LinkedHashSet<>();
String[] basePackagesArray = componentScan.getStringArray("basePackages");
for (String pkg : basePackagesArray) {
String[] tokenized = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.environment.resolvePlaceholders(pkg),
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
Collections.addAll(basePackages, tokenized);
}
for (Class<?> clazz : componentScan.getClassArray("basePackageClasses")) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
}
if (basePackages.isEmpty()) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(declaringClass));
}
scanner.addExcludeFilter(new AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter(false, false) {
@Override
protected boolean matchClassName(String className) {
return declaringClass.equals(className);
}
});
// 扫描包下的类文件
return scanner.doScan(StringUtils.toStringArray(basePackages));
}
根据注解扫描到需要被注入到容器中的bean
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
// 找到符合条件的bean,根据调用方法的不同,会有不同的匹配规则,比如携带@Component注解的
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
// 注册到容器中
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
3.7 注册 Bean 后处理器
3.8 初始化上下文的消息
3.9 初始化应用事件组播器
3.10 初始化webserver
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
3.11 检查并注册监听器
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
3.12 实例化所有剩余的Bean⭐
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 关键代码 实例化剩余的单例模式Bean
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
} else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
} else {
// 获取bean,具体代码看3.12.1 getBean
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
} else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
3.12.1 doGetBean⭐
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// 根据beanName尝试从单例池(一级缓存)中获取bean实例 3.12.2 getSingleton
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// 没有获取到实例
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// 判断是否存在循环依赖
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
// 创建实例
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 实例类型为单例模式
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
// 通用方法 3.12.3 createBean
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
// 实例为原型类型
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
// 其他类型
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean ´" + beanName + "'");
}
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
3.12.2 getSingleton ⭐⭐⭐
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
return getSingleton(beanName, true);
}
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
//
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
// 有米有发现这里使用了DCL(Double Check Lock)
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
// earlySingletonObjects是解决循环依赖的关键
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
3.12.3 createBean⭐
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 经过一系列判断,开始创建bean 3.12.4 doCreateBean
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
3.12.4 doCreateBean ⭐⭐
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建实例 3.12.5 createBeanInstance
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
3.12.5 createBeanInstance ⭐⭐
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
// 有工厂就用工厂创建
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
// 如果这个类之前被创建过
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// 如下就是构造bean的构造函数
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
// 考虑是否存在有需要自动装配的参数
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
// 指定构造函数
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
// 默认的空构造函数 3.12.6
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
3.12.6 instantiateBean⭐⭐⭐
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this),
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 先获取实例化策略,这里spring一般会选用cglib
// 然后实例化
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor<?> constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class<?> clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedExceptionAction<Constructor<?>>) clazz::getDeclaredConstructor);
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
// 发现最后还是使用了Beanutils工具
// 突然发现以后我们就可以直接使用这个工具类去利用反射去创建对象了
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}
4.1 运行SpringBoot上下文
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
总结
TIPS : BeanUtils.instantiateClass(),是一个很不错的Spring的工具类
